Currency prices in the Forex market are highly dynamic and influenced by a range of factors, from economic indicators to global events. Understanding what drives these fluctuations is crucial for traders looking to make informed decisions. Here are the key factors that affect currency prices:
1. Interest Rates

Central banks set interest rates, and these rates play a significant role in the value of a currency. When a country’s interest rates rise, its currency often appreciates as higher interest rates attract more foreign investment, increasing demand for that currency. Conversely, a reduction in interest rates can lead to forex currency depreciation.
2. Economic Indicators

Economic data releases, such as Gross Domestic Product (GDP), employment rates, and retail sales, are indicators of a country’s economic health. Strong economic performance tends to boost a country’s currency as it signals stability and growth. For example:
- GDP Growth: Higher GDP suggests a strong economy, attracting investors and strengthening the currency.
- Employment Data: A low unemployment rate is a positive indicator, potentially driving currency appreciation.
- Consumer Price Index (CPI) & Inflation: Higher inflation can lead to a weaker currency, as it erodes purchasing power. However, controlled inflation can encourage spending and growth, supporting the currency.
3. Political Stability and Events

Political uncertainty or instability, such as elections, changes in government policies, or geopolitical tensions, can lead to currency volatility. Traders tend to avoid currencies associated with countries experiencing political upheaval, while countries with stable governments generally have stronger currencies.
- Geopolitical Events: Wars, trade tensions, or diplomatic disputes can cause sudden price swings as they disrupt economic conditions.
- Elections: Upcoming elections can introduce uncertainty. Investors may pull back, causing currency fluctuations until results stabilize the outlook.
4. Market Sentiment and Speculation
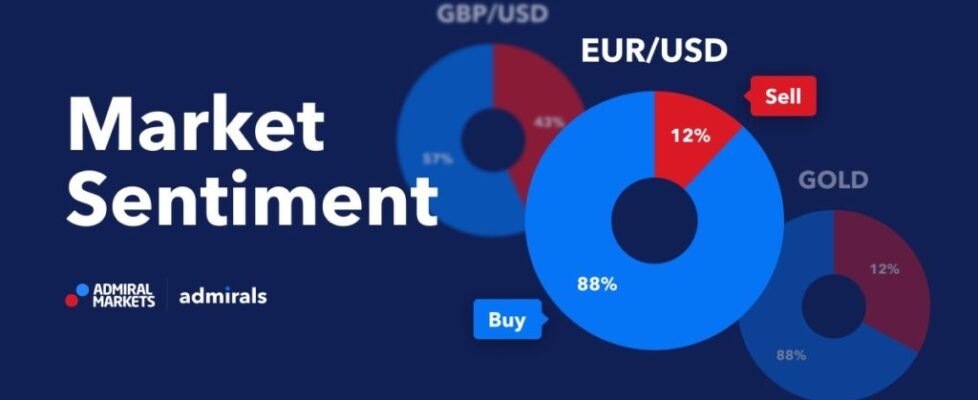
Forex is heavily influenced by market sentiment—how traders collectively feel about the economy and market direction. If traders expect a currency to rise, they will buy it, increasing demand and thus its price. On the other hand, if there is a negative outlook, traders will sell off, causing depreciation.
5. Trade Balance and Economic Policy
The balance of imports and exports can affect currency value. A country with a trade surplus (exports greater than imports) often sees its currency strengthen because demand for its goods requires more of its currency. Conversely, a trade deficit can lead to a weaker currency.
- Trade Agreements and Tariffs: Changes in trade policies can impact currency values. Positive trade agreements may boost a currency, while tariffs or trade restrictions can hurt it.
6. Global Economic Conditions
The global economy is interconnected, so economic changes in one country can impact others. A recession in a major economy like the United States or China, for example, can affect global currency markets. Additionally, global crises—like financial meltdowns, pandemics, or natural disasters—often result in currency shifts as investors seek safe-haven currencies, such as the US dollar or Swiss franc.
7. Natural Disasters
Unexpected events like earthquakes, floods, or pandemics can disrupt the economic stability of a country, causing its currency to depreciate as traders view it as a higher risk. Conversely, countries that are less affected may see their currencies appreciate as investors shift their investments.